Blog
Learn something good today!
Your guide to medicinal wellness

What happens during the various stages of menopause
Introduction
Menopause marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles and fertility. It involves several hormonal changes and menopausal symptoms at different stages of menopause. Let’s understand what actually happens during the various stages of menopause. The phase before menopause is called the perimenopause and the phase after menopause is called postmenopause.
Perimenopause
This phase starts several years before menopause. Here, the ovaries start producing less estrogen gradually through the time which is why you start getting your periods irregularly. You might notice that as time passes by, the gap in between your periods increases. Many may also start to experience the various menopausal symptoms like hot flashes that are sudden flares of heat and sweating, mood swings due to the hormone imbalances and vaginal dryness that leads to dry and irritated vulva. This phase is a transition to actual menopause and usually starts when you are in your 40s. As you are still having menstrual cycles during this time, you can still get pregnant.
Menopause
Now as your periods continue being irregular, menopause is when the occurrence of periods completely stops. Your estrogen levels have been dropped to a significant level and your menstrual cycle has completely ceased. Officially, menopause is declared after 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. Again, the symptoms of menopause continue to persist. On an average, menopause happens from ages 51-55.
Postmenopause
This is the phase after menopause that lasts for the rest of a woman’s life. This is where the estrogen levels have stabilized at a lower level and you might not experience most of the menopausal symptoms anymore. However, due to the low estrogen levels, postmenopausal women are more vulnerable to various health conditions like heart diseases and osteoporosis.
Before menopause, estrogen provides some protection against heart disease by helping to keep arteries flexible and promoting healthy levels of cholesterol. After menopause, when estrogen levels decline, this protective effect diminishes, hence leading to an increased risk of heart disease. To deal with it, it is important for women to maintain a healthy weight and opt for a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol.
Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density too. After menopause, the declining estrogen can lead to rapid bone loss and an increased risk of osteoporosis which results in weakened, brittle bones that are more susceptible to fractures. Hence it is important to intake calcium and vitamin D through diet or supplements.
Conclusion
Menopause is a journey that every woman has to go through in her life. Understanding what actually happens inside the body makes it easier for us to manage it. Getting educated about the various issues that one might face, gives us plenty of time to prepare for it and take lifestyle and treatment approaches that are suitable.
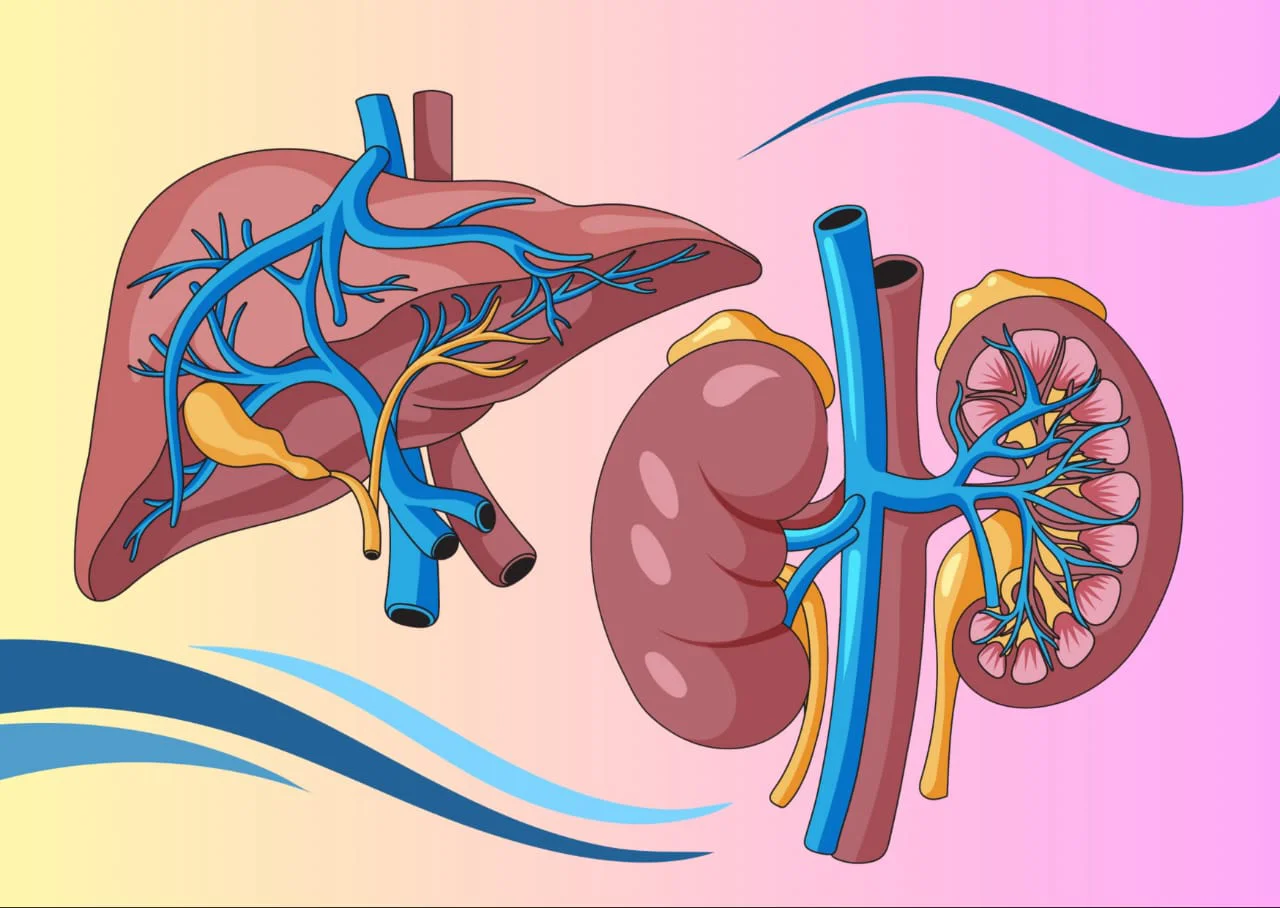
Your liver disease can affect you kidneys more than you think
Introduction
The liver is a remarkable organ known for its regenerative capabilities. It has the unique ability to repair and regenerate damaged tissue which enables it to recover from a wide range of injuries and insults. While the liver is indeed a regenerative organ with a remarkable capacity for self-repair, certain liver diseases can have detrimental effects on the kidney’s problems. It’s essential to monitor and manage liver diseases carefully as their progression can lead to kidney problems.
How liver and kidneys are related
The liver and kidneys are both involved in filtering and detoxifying the blood. The liver processes and metabolizes toxins, drugs and metabolic waste products from the bloodstream, converting many of them into water-soluble compounds that can be excreted by the kidneys. This collaboration helps eliminate waste and maintain the body’s internal environment.
The liver produces urea, a waste product of protein metabolism which is eventually excreted by the kidneys in the form of urine. This process helps regulate nitrogen balance in the body.
Both organs play a role in regulating blood pressure. The liver helps regulate blood volume by producing proteins like albumin, which maintains oncotic pressure. The kidneys regulate blood pressure by controlling the volume of blood and the balance of electrolytes and hormones such as renin and aldosterone.
How liver diseases can impact the kidneys
Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially life-threatening condition in which liver dysfunction often associated with advanced liver disease (cirrhosis) leads to kidney diseases and dysfunction. As liver function declines, it can cause changes in blood flow to the kidneys, leading to a reduction in normal kidney function and the development of HRS.
When the liver is damaged or unable to detoxify the blood effectively, toxins and waste products can build up in the bloodstream. These substances can place additional stress on the kidneys potentially leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) or worsening of existing kidney problems.
Liver diseases can result in fluid retention in the abdominal cavity known as ascites. The accumulation of excess fluid can increase pressure on the blood vessels and impair kidney function potentially leading to kidney diseases and dysfunction.
Liver diseases can disrupt the balance of electrolytes in the body such as sodium and potassium. These imbalances can affect normal kidney function and lead to complications like dehydration or electrolyte abnormalities.
Conclusion
Taking good care of your liver is really important for the health of your kidneys. Your liver is like a superhero that can fix itself when it gets hurt, but if it’s not working well because of various liver diseases, it can make your kidneys sick too. So it’s best to keep your liver healthy by seeing a doctor regularly, making healthy lifestyle choices and following any medical advice you get. This way, you’re not only helping your liver but also keeping your kidneys in good shape which is essential for your overall health

Guide to manage PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder affecting millions of women worldwide. Characterized by irregular periods, ovarian cysts and hormonal imbalances, PCOS can impact various aspects of a woman’s health and well-being. PCOS is often associated with insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain, difficulty losing weight and an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. Hormonal imbalances, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones), can cause acne, excessive hair growth and hair loss of the scalp. PCOS is a leading cause of infertility due to irregular ovulation. While there’s no cure for PCOS, adopting a healthy lifestyle helps to manage the condition.
Firstly it is very important to pay attention to the foods you consume. Opting for food that are nutrient-dense and whole foods like fruits, vegetables and lean proteins help in contributing to a healthier lifestyle while incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, nuts, seeds and leafy greens helps to reduce inflammation associated with PCOS. Further try to limit refined carbohydrates and sugars, which can spike insulin levels and exacerbate PCOS symptoms.
Exercise plays an important role in managing the weight gained due to PCOS. Not just that, but movement helps to make sure that insulin sensitivity is improved and stress levels are reduced, which all are beneficial for PCOS management. Try to incorporate as much as cardiovascular exercises, strength training and flexibility exercises into your routine. Find activities you enjoy, whether it’s dancing, swimming, any physical sport or yoga to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine.
Prioritize quality sleep by establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support hormone regulation. Minimize exposure to screens and stimulating activities before bedtime to promote better sleep quality.
Chronic stress can exacerbate PCOS symptoms by increasing cortisol levels and disrupting hormonal balance. Incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can help reduce stress. Practice mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises or yoga to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment, whether it’s spending time in nature, pursuing creative hobbies or connecting with loved ones. Prioritize self-care activities to nurture your physical and emotional well-being.
Lastly, consult your gynecologist regularly to stay updated on your progress in battling PCOS. Try to reach out to multiple women through online communities to share experiences and find encouragement from others facing similar challenges. Remember that small changes can lead to significant improvements over time so be patient and compassionate with yourself as you navigate your PCOS journey.

Understanding the Silent Struggle – Male Infertility
Introduction
When we think about infertility, the conversation often revolves around women and their reproductive health. However, it is essential to shed light on the silent struggle faced by men—male infertility. In this blog, we will explore the various aspects of male infertility, including its causes, effects, and the importance of raising awareness about this often-overlooked issue.
Unveiling Male Infertility
Male infertility refers to the inability of a man to contribute to a successful pregnancy after a year of regular, unprotected intercourse. It is a widespread concern, affecting millions of couples worldwide. In fact, male infertility contributes to nearly 40-50% of all infertility cases.
Understanding the Causes
Lets first understand the structure and function of the sperm. A sperm cell has a unique structure that is tailored for its specific function. It consists of three main parts – head, midpiece and tail (flagellum). The primary function of sperm is to fertilize the female egg. The nucleus of the sperm carries the genetic material in the form of DNA. It contains the instructions necessary for the development and functioning of an organism. During fertilization, the sperm’s nucleus fuses with the egg’s nucleus, combining the genetic material from both parents to create a new individual with a unique set of genes. The mitochondria, located in the midpiece of the sperm, provide the energy required for sperm motility and other cellular processes. They generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which serves as the energy currency of the cell. The mitochondria play a crucial role in powering the sperm’s swimming motion, allowing it to reach the egg.
Several factors can contribute to male infertility, including:
1. Low sperm count: A low sperm count, known as oligospermia, can hinder the chances of conception. This can be caused by various factors, such as hormonal imbalances, genetic conditions, testicular infections, or exposure to certain medications or toxins.
2. Poor sperm motility: Sperm with reduced motility or abnormal movement may struggle to reach and fertilize an egg. Factors like genetic disorders, infections, or lifestyle choices can impact sperm motility.
3. Abnormal sperm morphology: The shape and size of sperm can affect their ability to penetrate an egg. Genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, or environmental influences can contribute to abnormal sperm morphology.
4. Ejaculatory issues: Problems with ejaculation, such as retrograde ejaculation (when semen enters the bladder instead of being expelled) or erectile dysfunction, can make conception difficult.
5. Obstruction or blockages: Blockages in the male reproductive tract can prevent sperm from being ejaculated. These blockages can result from previous surgeries, infections, or congenital conditions.
Breaking the Silence: Raising Awareness
Despite its prevalence and significant impact, male infertility often remains a silent struggle due to societal expectations and misconceptions. Men may hesitate to seek help or share their experiences due to fear of judgment or societal pressures. Raising awareness about male infertility is crucial for breaking the silence and fostering a supportive environment. By encouraging open conversations, we can reduce stigma, provide a platform for individuals to share their stories, and offer support and understanding to those facing male infertility.
Conclusion
Male infertility is a common but often overlooked issue that impacts individuals and couples worldwide. By understanding its causes, effects, and the importance of raising awareness, we can create a supportive environment for those facing this silent struggle. It is crucial to break the silence, encourage open conversations, and seek professional help when needed. With the right support and available treatments, individuals and couples can navigate the challenges of male infertility and find hope on their path to parenthood.
